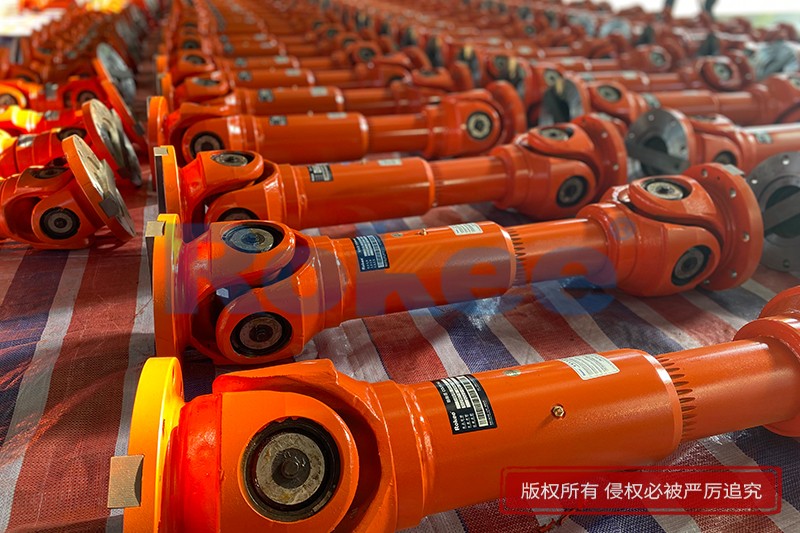
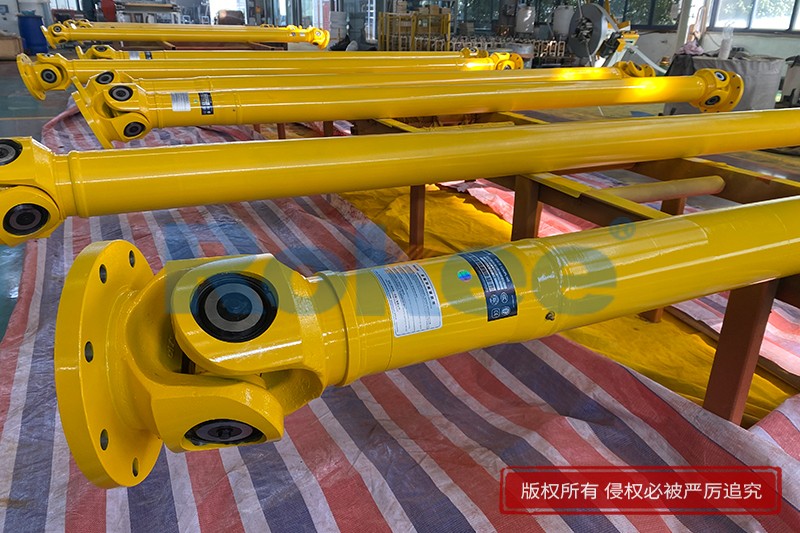
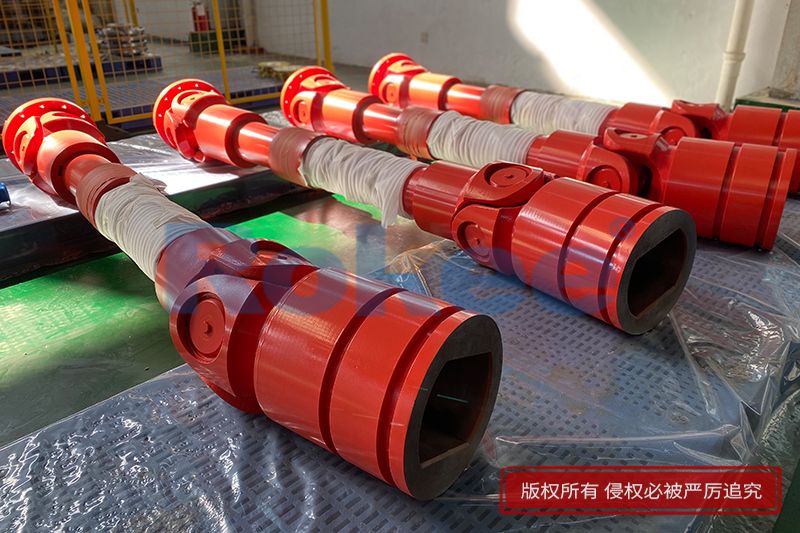
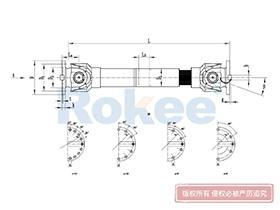
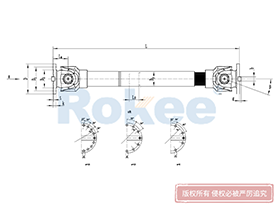
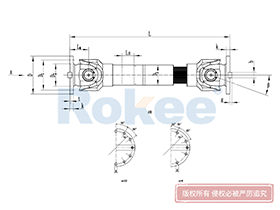
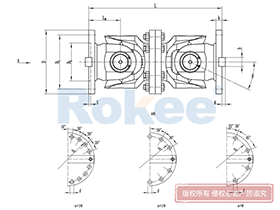
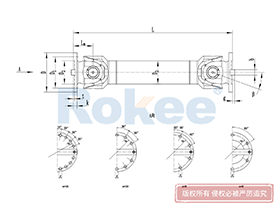
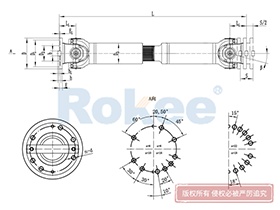
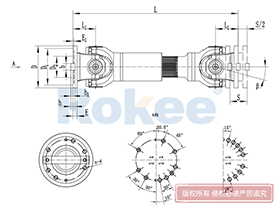
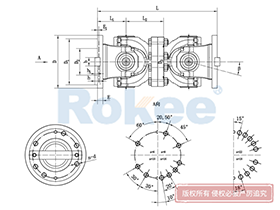
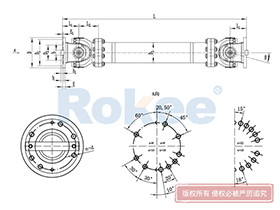
Industrial Cardan Shafts
Rokee is Industrial Cardan Shafts Manufacturer, Customizable according to the industrial cardan shafts drawings provided by the customer, Support Export.
Industrial Cardan Shafts are widely used and have many impressive records. From micro products for modern logistics, artificial intelligence machinery, light products used in the paper industry, high speed and high performance products for engineering and railway vehicles, to super heavy duty products used in metallurgical rolling system systems, Rokee has won us with mature products and quality Long-term trust of customers, widely exported to Europe, America and other parts of the world.
SWC-BH Universal Coupling
standard telescopic welded
View MoreSWC-CH Uuniversal Coupling
Long Telescopic Welded
View MoreSWC-DH Universal Coupling
Short Telescopic Welded
View MoreSWC-WD Universal Coupling
Non-telescopic Short
View MoreSWC-WH Universal Coupling
Non-telescopic Welded
View MoreSWP-A Universal Coupling
Long Type, Telescopic
View MoreSWP-B Universal Coupling
Short Type, Telescopic
View MoreSWP-C Universal Coupling
Short Type, Non-telescopic
View MoreSWP-D Universal Coupling
Long Type, Non-elescopic
View More
In the intricate ecosystem of industrial machinery, power transmission stands as a fundamental pillar that ensures the seamless operation of countless processes. From the heavy-duty rotations of steel rolling mills to the precise movements of paper manufacturing equipment, the ability to transfer rotational motion between non-coaxial shafts efficiently and reliably is indispensable. Among the various mechanical components designed for this purpose, the industrial cardan shaft emerges as a versatile and robust solution. Also known as a universal joint shaft, it is engineered to accommodate angular misalignments, absorb axial movements, and transmit high torque under demanding operating conditions.
1. Understanding the Industrial Cardan Shaft: Definition and Core Functions
At its core, an industrial cardan shaft is a mechanical assembly designed to transmit rotational motion and torque between two shafts that are not aligned on the same axis. Unlike rigid drive shafts, which require precise coaxial alignment to function effectively, the cardan shaft’s unique design allows it to compensate for angular deviations, axial displacements, and even slight parallel misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. This flexibility makes it an ideal component in applications where equipment positioning constraints, thermal expansion, or dynamic movements prevent perfect shaft alignment.
The primary functions of an industrial cardan shaft can be summarized as follows: first, to transmit torque from the power source (such as an electric motor or engine) to the driven machinery with minimal energy loss; second, to accommodate angular misalignment between connected shafts, which can range from a few degrees up to 45 degrees depending on the design type; third, to absorb axial movements caused by thermal expansion or contraction of machinery components during operation; and fourth, to minimize vibration and noise, thereby enhancing the stability and lifespan of the entire transmission system. These functions collectively make the cardan shaft a critical component in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of industrial processes.
2. Structural Composition of the Industrial Cardan Shaft
An industrial cardan shaft is a modular assembly composed of several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring its overall performance and durability. While designs may vary based on specific application requirements, the core components remain consistent across most configurations. The following sections detail the primary elements of a typical industrial cardan shaft:
2.1 Universal Joint (U-Joint)
The universal joint, often referred to as the U-joint, is the central component that enables the cardan shaft’s flexibility. It consists of a cross-shaped intermediate member (known as the spider or cross) and four needle bearings housed within bearing cups. The spider’s four arms (journals) fit into the bearing cups, which are in turn attached to the yokes of the connected shafts. This configuration allows the U-joint to pivot freely, enabling the transmission of rotational motion between shafts at different angles. In applications requiring constant output velocity, two U-joints are typically used in series, with the yokes aligned to counteract velocity fluctuations inherent in single U-joint designs. This double U-joint arrangement ensures smooth and consistent torque transmission even at maximum misalignment angles.
2.2 Yokes
Yokes are U-shaped components that serve as the connection points between the universal joint and the driving/driven shafts. They are typically forged from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys to withstand the high torque and stress encountered during operation. Each yoke features two forked arms with holes that accommodate the bearing cups of the U-joint. The design of the yoke must be precise to ensure a secure fit with the U-joint and the connected shafts, as any looseness or misalignment can lead to vibration, noise, and premature wear. Yokes can be either integral (machined directly onto the shaft) or flanged (attached to the shaft via bolts), depending on the application’s mounting requirements.
2.3 Shaft Tube
The shaft tube is the outer casing of the cardan shaft, providing structural support and protecting the internal components from external contaminants such as dust, dirt, and moisture. It is typically constructed from seamless steel or aluminum tubing, chosen for its high strength-to-weight ratio. In heavy-duty applications, the shaft tube may be thickened or reinforced to handle higher torque loads. For longer cardan shafts, the shaft tube is often hollow to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity, which helps minimize vibration and energy consumption. The length of the shaft tube is customized based on the distance between the driving and driven shafts, with some designs capable of transmitting torque over distances exceeding 30 meters.
2.4 Slip Joint
The slip joint, also known as the telescopic joint, is a critical component that accommodates axial movements between the connected shafts. It consists of a splined shaft and a splined yoke, which fit together to allow the shaft to extend and contract freely. This flexibility is essential for compensating for changes in shaft length caused by thermal expansion, vibration, or relative movement between machinery components. The splined connection ensures that torque is transmitted efficiently even as the joint slides, with lubrication applied to minimize friction and wear. In some designs, the slip joint is integrated into one of the yokes, while in others, it is a separate component located in the middle of the shaft tube.
2.5 Center Support Bearing
For longer cardan shafts (typically those exceeding 3 meters in length), a center support bearing is used to provide additional stability and reduce vibration. This bearing is mounted on a bracket that is secured to the machinery frame, supporting the middle section of the shaft tube. The center support bearing helps distribute the weight of the shaft evenly, preventing sagging and reducing stress on the U-joints. It is typically a ball or roller bearing designed to withstand radial loads, with a sealed housing to protect against contamination and retain lubrication. The use of a center support bearing extends the lifespan of the cardan shaft and ensures smooth operation at high rotational speeds.
2.6 Flanges
Flanges are flat, circular components used to connect the cardan shaft to the driving or driven machinery. They feature multiple bolt holes that allow for secure attachment, ensuring a rigid connection that can withstand high torque loads. Flanges are typically made from the same high-strength materials as the yokes, with precise machining to ensure alignment with the shaft and machinery. In some applications, flexible flanges (incorporating rubber or elastomeric elements) may be used to absorb shock and vibration, further enhancing the smoothness of power transmission.
3. Working Principles of the Industrial Cardan Shaft
The operation of an industrial cardan shaft is based on the principle of transmitting rotational motion through a series of pivoting joints, allowing for misalignment between the driving and driven shafts. The basic working mechanism can be broken down into the following steps:
1. Torque Input: The driving shaft (connected to a power source such as an electric motor) rotates, transferring motion to the attached yoke. This yoke is connected to one end of a universal joint, causing the spider of the U-joint to rotate.
2. Motion Transmission Through U-Joint: As the spider rotates, its four journals (fitted with needle bearings) transmit the rotational motion to the opposing yoke. The U-joint’s design allows the spider to pivot, enabling the opposing yoke to rotate even if it is at an angle relative to the driving yoke.
3. Torque Output to Driven Shaft: The opposing yoke (connected to the driven shaft) converts the pivoting motion of the U-joint back into rotational motion, driving the driven machinery. In applications using two U-joints (double cardan shaft), the second U-joint compensates for any velocity fluctuations introduced by the first, ensuring that the driven shaft rotates at a constant speed, even when the angle between the shafts changes.
4. Compensation for Axial Movement: The slip joint allows the cardan shaft to extend or contract as needed, accommodating axial displacements between the driving and driven shafts. This ensures that the U-joints remain properly engaged and that torque transmission is not interrupted, even as the relative position of the shafts changes due to thermal expansion or vibration.
A key consideration in the working principle of the cardan shaft is the issue of velocity fluctuation. A single U-joint causes the driven shaft to accelerate and decelerate slightly as it rotates, especially at large misalignment angles. This fluctuation can lead to vibration and noise, which is undesirable in many industrial applications. To address this, the double cardan shaft configuration is used, where two U-joints are aligned such that the velocity fluctuations from the first U-joint are canceled out by the second. This results in constant output velocity, making the double cardan shaft suitable for high-speed applications such as paper mills and precision manufacturing equipment.
4. Key Applications of Industrial Cardan Shafts
The industrial cardan shaft’s unique combination of flexibility, high torque capacity, and durability makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. From heavy-duty manufacturing to marine propulsion, it plays a critical role in ensuring the efficient operation of machinery across diverse sectors. The following sections highlight the most prominent applications of industrial cardan shafts:
4.1 Steel Manufacturing Industry
The steel manufacturing industry is one of the most demanding environments for power transmission components, with machinery operating under high torque, high temperature, and heavy load conditions. Industrial cardan shafts are extensively used in rolling mills, where they transmit torque from electric motors to the rolling stands. Rolling mills require precise power transmission to ensure uniform thickness of steel sheets, bars, or rails, and the cardan shaft’s ability to accommodate misalignment caused by thermal expansion and vibration is essential. Additionally, cardan shafts are used in other steel mill equipment such as continuous casters, conveyors, and scrap metal processing machines, where their robustness and reliability are critical for minimizing downtime.
4.2 Paper and Pulp Industry
In the paper and pulp industry, high-speed machinery such as paper machines, calenders, and winders rely on efficient power transmission to maintain consistent production. Industrial cardan shafts are used to connect the main drive motor to the various sections of the paper machine, including the forming section, pressing section, and drying section. These applications require constant velocity transmission to ensure uniform paper thickness and surface quality, making the double cardan shaft configuration particularly suitable. The cardan shaft’s ability to accommodate misalignment between the drive components and the paper machine sections, which may shift slightly due to thermal expansion, is crucial for preventing paper defects and ensuring smooth operation.
4.3 Construction and Mining Machinery
Construction and mining machinery operate in harsh, off-road environments where equipment is subjected to extreme vibrations, shocks, and misalignment. Industrial cardan shafts are used in excavators, backhoes, bulldozers, tractors, and mining trucks to transmit torque from the engine to the wheels or tracks. These applications require cardan shafts with high torque capacity and robust construction to withstand the heavy loads and dynamic forces encountered during operation. The slip joint component is particularly important in these machines, as it accommodates the axial movements caused by the suspension system and terrain irregularities. Additionally, the cardan shaft’s ability to operate at large misalignment angles ensures that power is transmitted efficiently even when the machinery is in uneven terrain.
4.4 Marine Propulsion Systems
Marine propulsion systems rely on industrial cardan shafts to transmit torque from the engine to the propeller. The marine environment presents unique challenges, including corrosion, moisture, and the need to accommodate misalignment between the engine and the propeller shaft. Cardan shafts used in marine applications are typically constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, with sealed bearings to prevent water ingress. They are designed to handle high torque loads and accommodate the angular misalignment caused by the movement of the ship’s hull in rough seas. Additionally, marine cardan shafts may incorporate flexible couplings to absorb shock and vibration, enhancing the smoothness of propulsion and reducing stress on the engine and propeller.
4.5 Wastewater Treatment and Pumping Systems
Wastewater treatment plants and pumping systems use industrial cardan shafts to drive pumps, mixers, and aerators. These applications require reliable power transmission in corrosive and wet environments, with cardan shafts designed to resist rust and contamination. The cardan shaft’s ability to accommodate misalignment between the motor and the pump is essential, as these components may shift slightly during installation or operation. Additionally, the low maintenance requirements of modern cardan shafts make them ideal for wastewater treatment plants, where minimizing downtime is critical for ensuring continuous operation.
4.6 Amusement and Entertainment Industry
The amusement and entertainment industry uses industrial cardan shafts in rides such as roller coasters, Ferris wheels, and carousels. These applications require precise power transmission to ensure the safety and smooth operation of the rides. Cardan shafts are used to connect the drive motors to the ride mechanisms, accommodating misalignment and absorbing vibration to provide a comfortable experience for riders. The compact design of cardan shafts makes them suitable for the tight spaces often found in amusement ride installations, while their durability ensures reliable operation even with frequent start-stop cycles.
5. Maintenance Practices for Industrial Cardan Shafts
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long lifespan, efficiency, and reliability of industrial cardan shafts. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear, vibration, noise, and even catastrophic failure, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. The following maintenance practices are recommended for industrial cardan shafts:
5.1 Regular Inspection
Regular visual and physical inspections should be conducted to identify signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspections should include checking the flange bolts for tightness, as loose bolts can cause misalignment and vibration. Additionally, the U-joints should be inspected for backlash (excessive play), which indicates worn bearings or spider journals. Any unusual noise or vibration during operation should be investigated immediately, as these are common indicators of component failure. Inspections should be conducted at least once a year, with more frequent checks for cardan shafts operating in harsh environments (such as high temperature, dust, or moisture).
5.2 Lubrication
Lubrication is critical for reducing friction and wear in the U-joints, slip joints, and center support bearings. Most industrial cardan shafts are lubricated with grease, typically a lithium complex grease that meets industry standards. Grease nipples (located on the U-joint cross or bearing cups) should be cleaned before re-lubrication to prevent contamination. The grease should be applied until it flows out of the seals, ensuring that all bearing surfaces are fully lubricated. Over-lubrication should be avoided, as it can cause excess pressure and damage the seals. Cardan shafts that have been stored for more than six months should be re-lubricated before use. It is important to note that grease containing moly cote additives should not be used in most cardan shaft applications, as it can cause premature bearing failure.
5.3 Cleaning
Industrial cardan shafts should be kept clean to prevent the buildup of dust, dirt, and debris, which can damage seals and bearings. Cleaning should be done using a soft brush and mild detergent, avoiding aggressive chemical cleaners, pressurized water, or steam jets, as these can damage the seals and allow water or dirt to penetrate the internal components. After cleaning, the cardan shaft should be re-lubricated to ensure that the seals are properly coated and protected.
5.4 Alignment Checks
Proper alignment of the driving and driven shafts is essential for the efficient operation of the cardan shaft. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the U-joints, leading to premature wear and vibration. Alignment checks should be conducted during installation and periodically during operation, especially after any maintenance or machinery movement. The alignment should be checked both radially (parallel misalignment) and angularly (angular misalignment), with adjustments made as necessary to ensure that the shafts are within the recommended alignment tolerances.
5.5 Replacement of Worn Components
Worn or damaged components should be replaced immediately to prevent further damage to the cardan shaft and connected machinery. Common worn components include U-joint bearings, spider journals, yokes, and seals. When replacing components, it is important to use parts that meet the original design specifications, as non-standard parts can compromise the performance and durability of the cardan shaft. Additionally, the replacement process should be conducted by trained personnel to ensure proper installation and alignment.
6. Evolving Trends in Industrial Cardan Shaft Design and Technology
The industrial cardan shaft has evolved significantly since its invention, with advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and design techniques driving improvements in performance, durability, and efficiency. The following trends are shaping the future of industrial cardan shaft technology:
6.1 Lightweight Materials
There is a growing trend toward the use of lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys and composite materials in cardan shaft construction. These materials offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, reducing the overall weight of the shaft and minimizing energy consumption. Lightweight cardan shafts are particularly beneficial in mobile applications such as construction machinery and automotive vehicles, where reducing weight improves fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Additionally, composite materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for marine and wastewater treatment applications.
6.2 Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Advancements in manufacturing processes such as forging, machining, and 3D printing are improving the precision and durability of cardan shaft components. Forging processes are being optimized to produce yokes and U-joint spiders with superior strength and fatigue resistance, while CNC machining ensures precise dimensional accuracy, reducing the risk of misalignment. 3D printing is emerging as a viable technology for producing custom cardan shaft components, allowing for complex designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This technology also enables rapid prototyping, reducing the time required to develop new cardan shaft designs for specific applications.
6.3 Maintenance-Free Designs
Manufacturers are developing maintenance-free cardan shaft designs that reduce the need for regular lubrication and inspection. These designs incorporate sealed U-joints with lifetime lubrication, eliminating the need for re-lubrication. Additionally, self-aligning bearings and wear-resistant materials are being used to extend the lifespan of components, reducing the frequency of replacement. Maintenance-free cardan shafts are particularly beneficial in applications where access is difficult or where minimizing downtime is critical, such as offshore wind turbines and remote mining operations.
6.4 Smart Monitoring Systems
The integration of smart monitoring systems into industrial cardan shafts is becoming increasingly common. These systems use sensors to measure temperature, vibration, and torque, providing real-time data on the shaft’s performance. This data is transmitted to a central monitoring system, allowing operators to detect potential issues such as bearing wear, misalignment, or overloading before they lead to failure. Smart monitoring systems enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving the overall efficiency of the transmission system. Additionally, these systems can be integrated with industrial IoT (Internet of Things) platforms, enabling remote monitoring and control of cardan shaft performance.
6.5 High-Torque and High-Speed Capabilities
As industrial machinery becomes more powerful and efficient, there is a growing demand for cardan shafts with higher torque and speed capabilities. Manufacturers are responding by developing cardan shafts with larger diameters, reinforced components, and advanced bearing designs that can withstand higher loads and rotational speeds. These high-performance cardan shafts are suitable for applications such as large-scale steel rolling mills, marine propulsion systems, and power generation equipment, where high torque and speed are required.
7. Conclusion
The industrial cardan shaft is a vital component in modern power transmission systems, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and durability in a wide range of industrial applications. From its core components such as the universal joint and yokes to its advanced designs incorporating lightweight materials and smart monitoring systems, the cardan shaft has evolved to meet the changing needs of the industrial sector. Its ability to transmit torque between non-coaxial shafts, accommodate misalignment, and absorb axial movements makes it indispensable in industries such as steel manufacturing, paper production, construction, marine propulsion, and wastewater treatment.
Proper maintenance practices, including regular inspection, lubrication, and alignment checks, are essential for ensuring the long lifespan and efficient operation of industrial cardan shafts. As technology continues to advance, the future of cardan shaft design promises even greater efficiency, durability, and intelligence, with lightweight materials, maintenance-free designs, and smart monitoring systems leading the way.
In conclusion, the industrial cardan shaft remains a cornerstone of modern industrial machinery, playing a critical role in ensuring the seamless and reliable transmission of power. Its versatility and adaptability make it an essential component in the global industrial landscape, and its continued evolution will undoubtedly contribute to the efficiency and sustainability of industrial processes in the years to come.
« Industrial Cardan Shafts » Post Date: 2024/1/15
URL: http://www.rokee.com/en/tags/industrial-cardan-shafts.html