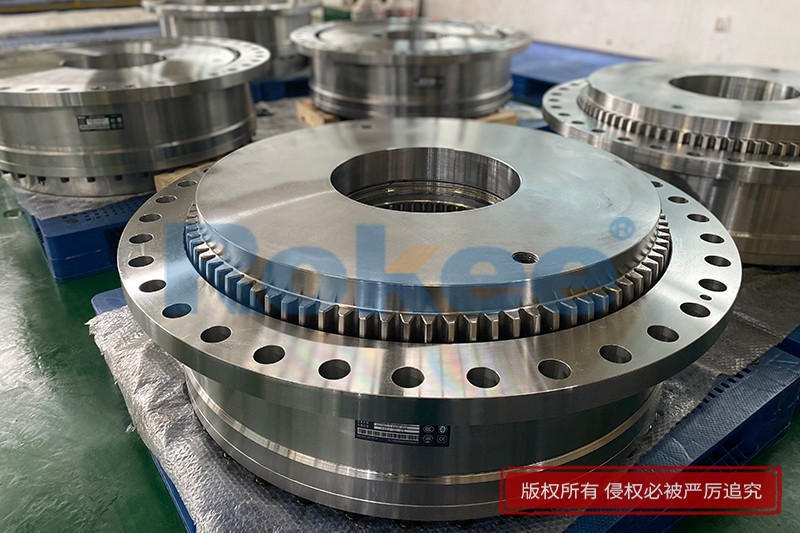
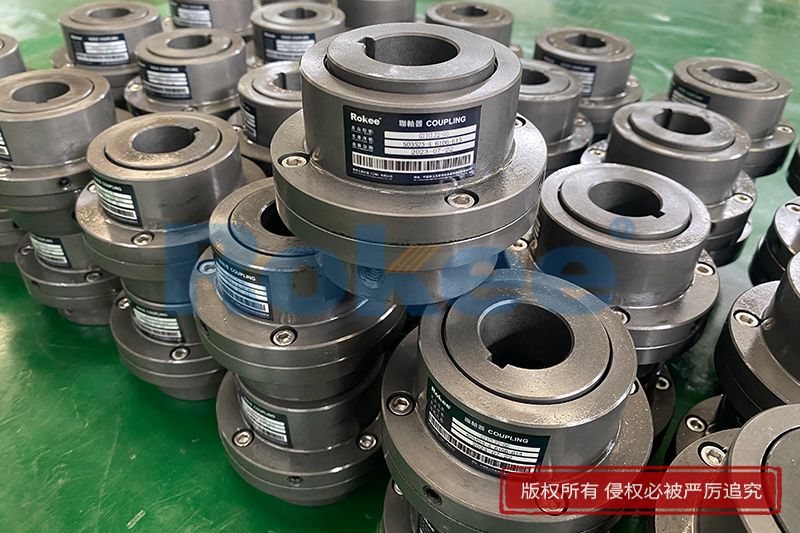
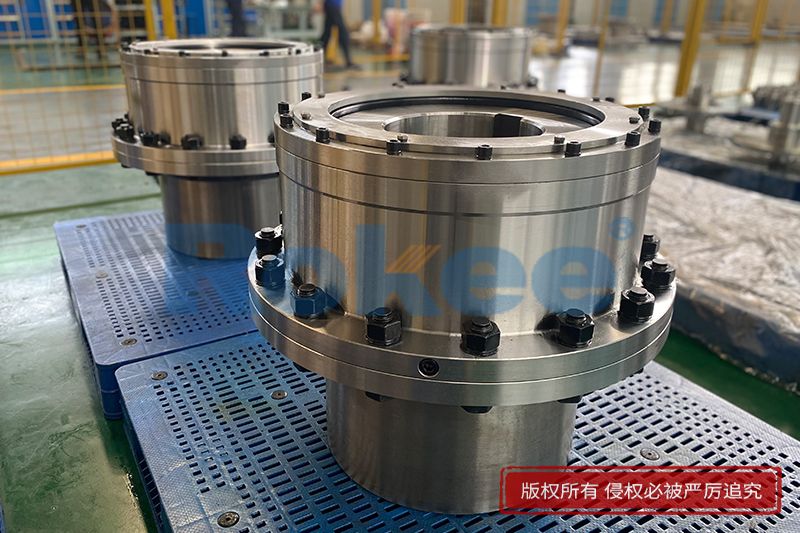
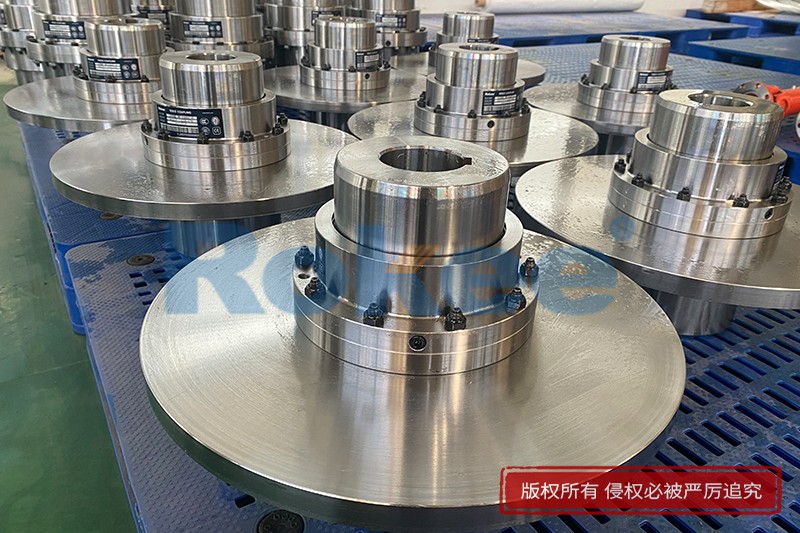
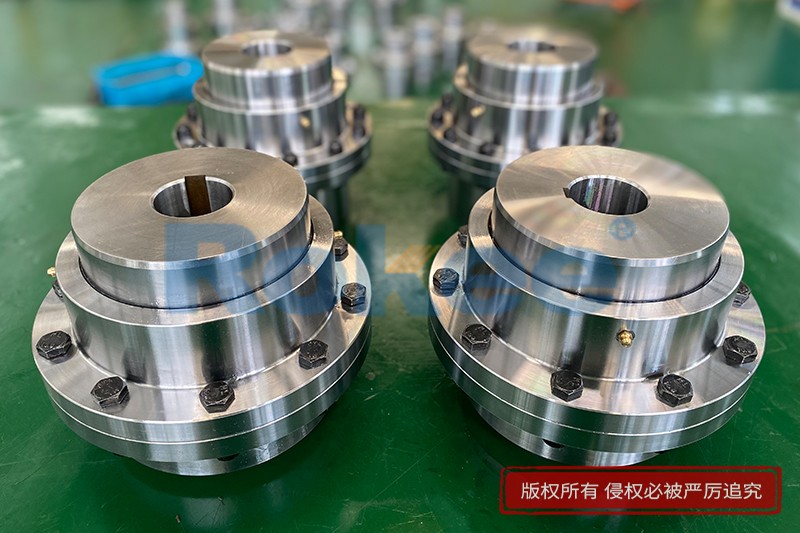
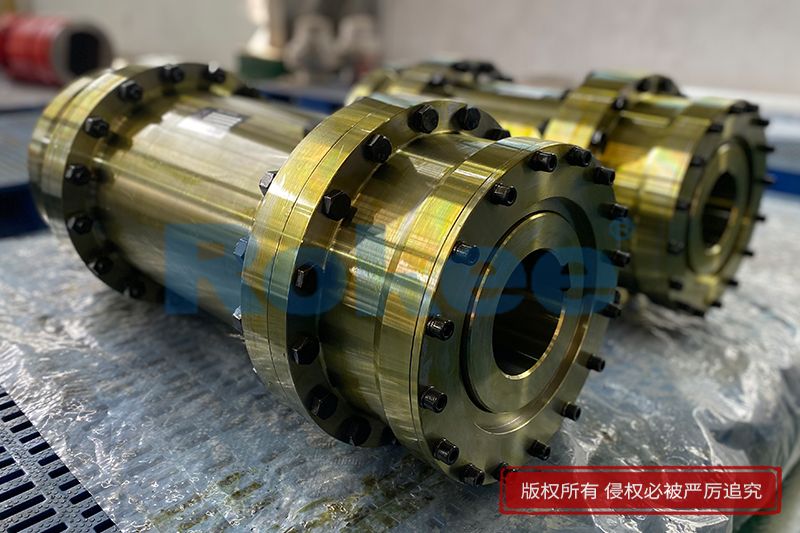
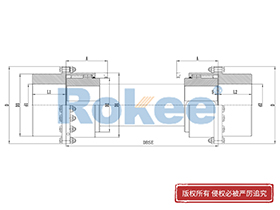
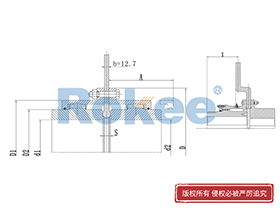
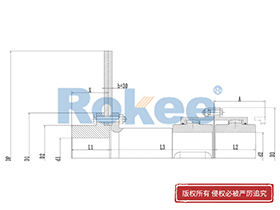
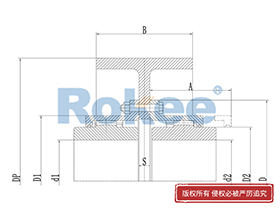
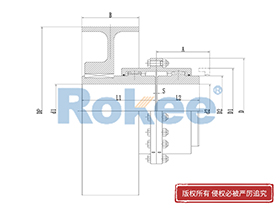
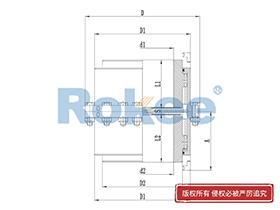
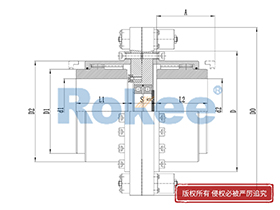
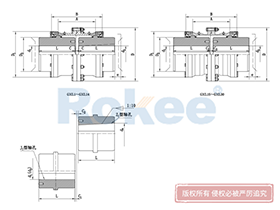
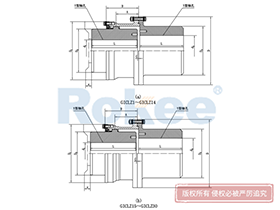
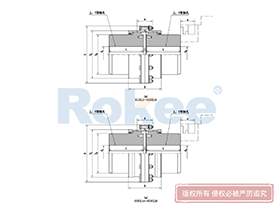
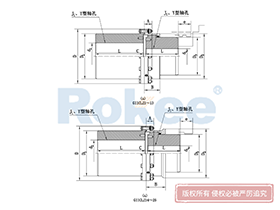
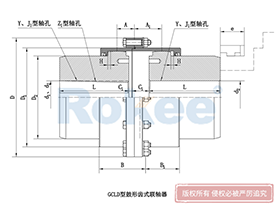
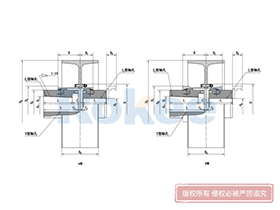
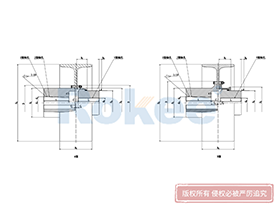
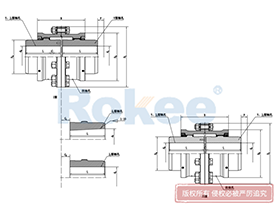
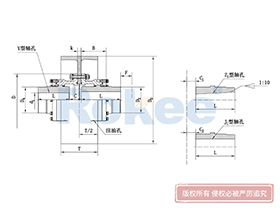
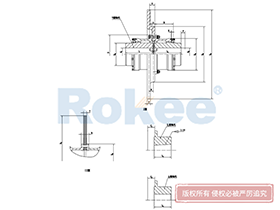
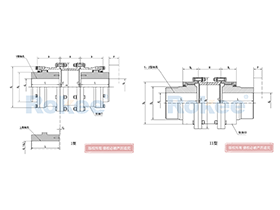
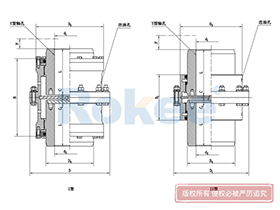
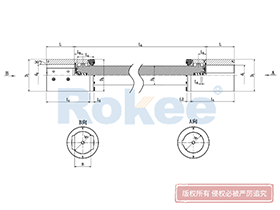
Curved Tooth Gear Couplings
Rokee is Curved Tooth Gear Couplings Manufacturer, Customizable according to the curved tooth gear couplings drawings provided by the customer, Support Export.
Curved Tooth Gear Coupling can be applied into various general drive sites. Due to the special hook face drum gear design, in the definitive deviation scope, Curved Tooth Gear Coupling can effectively avoid the edge stress concentration at tooth meshing, so Curved Tooth Gear Coupling has outstanding radial and angular centering capacity. Moreover, Curved Tooth Gear Coupling can ensure long service life.
RODX Drum Gear Coupling
Intermediate Connecting Shaft
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance.View MoreRODP Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Discs
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes.View MoreRODF Drum Gear Coupling
Split Type, Brake Disc
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes.View MoreRODW Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Wheel
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes.View MoreRODU Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Wheel
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance.View MoreRODV Drum Gear Coupling
Vertical Installation
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque.View MoreRODM Drum Gear Coupling
Torsion Protection
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.View MoreGICL Drum Gear Coupling
Wide
GICL Drum Gear Coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement.View MoreGICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Connected to Intermediate Shaft
Half of the GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement.View MoreGIICL Drum Gear Coupling
Narrow
GIICL Drum Gear Coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.View MoreGIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Connected to Intermediate Shaft
Half of the GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.View MoreGCLD Drum Gear Coupling
Motor Shaft Extension
GCLD Drum Gear Coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure.View MoreNGCL Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Wheel
NGCL Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.View MoreNGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Wheel
NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking.View MoreWG Drum Gear Coupling
Basic
The overall characteristics of WG Drum Gear Coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque.View MoreWGZ Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Wheel
WGZ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking.View MoreWGP Drum Gear Coupling
With Brake Discs
WGP Drum Gear Coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking.View MoreWGT Drum Gear Coupling
Intermediate Connecting Pipe
WGT Drum Gear Coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer.View MoreWGC Drum Gear Coupling
Vertical Installation
WGC Drum Gear Coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems.View MoreWGJ Drum Gear Coupling
Connected to Intermediate Shaft
WGJ Drum Gear Coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers.View More
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as critical components that bridge rotating shafts, enabling torque transfer while accommodating inevitable misalignments. Among the diverse range of couplings available, the curved tooth gear coupling stands out as a high-performance solution tailored for demanding industrial environments. Characterized by its unique tooth profile and robust construction, this type of coupling has become indispensable in applications requiring reliable torque transmission, excellent misalignment compensation, and long service life.
1. Fundamental Concepts and Design Principles
A curved tooth gear coupling is a rigid-flexible coupling that transmits torque through the meshing of curved external teeth on the hub and internal teeth on the sleeve. Unlike straight tooth gear couplings, its defining feature lies in the spherical curvature of the external teeth, with the center of the sphere coinciding with the axis of the gear. This curved tooth design is not arbitrary but a result of precise engineering calculations aimed at optimizing load distribution and misalignment accommodation.
The core design principles of curved tooth gear couplings revolve around three key objectives: maximizing torque transmission capacity, enhancing misalignment compensation capability, and minimizing wear and tear. To achieve these goals, the tooth clearance of curved tooth gear couplings is typically larger than that of straight tooth counterparts. This increased clearance not only facilitates smoother meshing under misalignment conditions but also helps in accommodating thermal expansion and contraction of shafts during operation. Additionally, many curved tooth gear couplings adopt a large pressure angle design, which contributes to a more compact structure, reduced length-diameter ratio, and improved speed performance. The overall structure is often optimized to ensure a coordinated proportion between the hole diameter and length, resulting in lightweight construction and low rotational inertia.
2. Structural Composition and Working Mechanism
The basic structure of a curved tooth gear coupling consists of four main components: two hubs with external curved teeth, two sleeves with internal teeth, and connecting bolts. The hubs are mounted on the drive and driven shafts respectively, usually via interference fit or keyway connection. The sleeves, which house the internal teeth, mesh with the external curved teeth of the hubs. The two sleeves are then fastened together using bolts to form a rigid connection, enabling torque transfer from the drive shaft to the driven shaft through the meshing teeth.
The working mechanism of curved tooth gear couplings is rooted in the curved tooth meshing principle. When the drive shaft rotates, the external curved teeth of the drive hub engage with the internal teeth of the sleeve, converting rotational motion into torque transfer. A key advantage of this mechanism is its ability to avoid edge pressure on the tooth surface during angular and radial misalignments. In straight tooth couplings, misalignment often leads to concentrated edge pressure on the tooth contact surfaces, resulting in severe wear. In contrast, the curved tooth profile ensures that the contact between the external and internal teeth is distributed over a larger area, even when shafts are misaligned. This uniform load distribution not only reduces wear but also enhances the coupling's ability to transmit higher torques.
Another important aspect of the working mechanism is the coupling's capacity to compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments. Axial misalignment occurs when the shafts move along their axial direction; radial misalignment is caused by the offset of the shaft centers; and angular misalignment arises when the shafts are not collinear. The spherical curvature of the external teeth, combined with the appropriate tooth clearance, allows the coupling to accommodate these misalignments by enabling slight relative movements between the meshing teeth. This compensation capability is crucial for protecting other components in the transmission system, such as bearings and gears, from excessive stress and premature failure.
3. Classification of Curved Tooth Gear Couplings
Curved tooth gear couplings can be classified into several types based on their tooth structure, design configuration, and application requirements. The following are the most common classifications:
3.1 Single Curve vs. Double Curve Couplings
Single curve couplings feature a single set of curved teeth on each hub. This basic design is suitable for light to mid-duty applications with lower torque loads. They are easy to install and offer basic power transmission and misalignment compensation capabilities. Double curve couplings, on the other hand, are equipped with two sets of curved teeth on each hub, resulting in two contact points between the meshing teeth. This design significantly improves torque transmission efficiency and load-carrying capacity, making double curve couplings ideal for heavy-duty and high-demand applications.
3.2 Compound Curve Couplings
Compound curve couplings combine the features of single and double curve designs, with one part of the coupling having single curved teeth and the other part having double curved teeth. This hybrid structure provides enhanced flexibility, making it particularly suitable for high-precision drive systems where precise alignment and torque transmission are critical. The additional flexibility offered by compound curve couplings helps in correcting misalignments more effectively, ensuring smooth operation of precision machinery.
3.3 Skeletal Curved Couplings
Skeletal curved couplings are designed with a lightweight structure, using a few supporting elements instead of a full solid construction. They have small clearances between the joints, which allows for relative motion while maintaining sufficient flexibility. Due to their lightweight and compact design, skeletal curved couplings are commonly used in sensitive equipment where space is limited. Despite their low load-bearing capacity, they exhibit significant damping capabilities, making them suitable for applications where vibration reduction is important.
3.4 Specialized Curved Tooth Couplings
In addition to the above types, there are specialized curved tooth couplings designed for specific applications. For example, vertical installation curved tooth couplings are tailored for vertical transmission systems, featuring a modified structure to accommodate the unique load distribution of vertical shafts. Couplings with brake wheels are another specialized type, designed for applications requiring braking functionality. These couplings integrate a brake wheel into the sleeve structure, allowing for quick and reliable braking of the transmission system.
4. Material Selection for Curved Tooth Gear Couplings
The performance and service life of curved tooth gear couplings are heavily dependent on the selection of appropriate materials. The choice of materials is determined by various factors, including the operating torque, speed, temperature, environmental conditions (such as corrosion and humidity), and load characteristics. The following are the commonly used materials for different components of curved tooth gear couplings:
4.1 Hub and Sleeve Materials
The hubs and sleeves, which bear the brunt of the torque transmission and tooth meshing, are typically made of high-quality alloy steels. Commonly used alloys include 42CrMo and 35CrMo, which offer excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, toughness, and wear resistance. These steels undergo quenching and tempering heat treatment, resulting in a tooth surface hardness of HRC 28-32, which balances wear resistance and toughness. For the internal tooth sleeves, 45 steel or 40Cr is often used, with a tempering treatment to achieve a hardness of HB 220-250, ensuring good meshing performance with the external curved teeth.
4.2 Materials for Special Environments
In corrosive environments, such as marine, chemical, or coastal applications, stainless steel is preferred for the hubs and sleeves. Stainless steel materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring the coupling's performance is not compromised by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or saltwater. For high-temperature applications, such as in gas turbines or industrial furnaces, heat-resistant steels are used. These steels can maintain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, preventing deformation and failure under extreme heat conditions.
4.3 Other Component Materials
The connecting bolts are typically made of high-strength alloy steels, such as 35CrMoA, to ensure they can withstand the clamping force required to fasten the sleeves together. Sealing components, such as O-rings, are made of rubber or synthetic materials that offer good elasticity and resistance to lubricants and high temperatures. The choice of sealing materials is crucial for preventing lubricant leakage and protecting the tooth meshing area from contamination by dust, dirt, or moisture.
5. Industrial Applications of Curved Tooth Gear Couplings
Due to their excellent torque transmission capacity, misalignment compensation capability, and robust construction, curved tooth gear couplings find widespread applications across various industrial sectors. The following are the key application areas:
5.1 Power Generation Industry
In the power generation sector, curved tooth gear couplings are extensively used in turbines, generators, and auxiliary equipment. These couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque from the turbine to the generator, accommodating misalignments caused by thermal expansion and contraction of the shafts during operation. Their ability to handle high torques and absorb shocks ensures the reliable operation of power generation equipment, which is essential for maintaining a stable power supply. Curved tooth gear couplings are also used in wind power generation systems, where they connect the wind turbine rotor to the generator, accommodating the dynamic misalignments caused by wind fluctuations.
5.2 Metallurgical Industry
The metallurgical industry, which includes steel and non-ferrous metal production, relies heavily on heavy-duty machinery such as rolling mills, crushers, and conveyors. These machines operate under high torque, high speed, and severe misalignment conditions, making curved tooth gear couplings an ideal choice. In rolling mills, for example, the couplings transmit torque from the motor to the rolling rolls, accommodating the misalignments caused by the heavy loads and thermal expansion of the rolls. Their robust construction and wear resistance ensure long service life in the harsh, dusty environment of metallurgical plants.
5.3 Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, curved tooth gear couplings are used in drilling rigs, extraction machinery, pumps, and compressors. Drilling rigs, in particular, operate under extreme conditions with high torque, shock loads, and significant misalignments. Curved tooth gear couplings transmit torque from the drill motor to the drill string, accommodating the dynamic misalignments caused by the movement of the rig and the uneven terrain. In addition, their ability to withstand corrosive environments makes them suitable for offshore oil and gas applications, where exposure to saltwater and humidity is inevitable.
5.4 Construction and Mining Industries
Construction and mining machinery, such as excavators, loaders, mining trucks, and crushers, operate in harsh and dynamic environments. Curved tooth gear couplings are used in these machines to transmit torque between the engine and the working components, such as the hydraulic pump or the transmission system. Their ability to absorb shocks and accommodate angular misalignments makes them ideal for these applications, where the machinery is constantly moving and subjected to variable loads. The robust construction of curved tooth gear couplings ensures they can withstand the impact and vibration associated with construction and mining operations.
5.5 Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, curved tooth gear couplings are used in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and control actuators. These applications require high reliability, precision, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures. Curved tooth gear couplings transmit power efficiently while absorbing shocks and dampening vibrations, ensuring the smooth operation of critical aerospace machinery. Their compact design and low rotational inertia are also advantageous in aerospace applications, where weight and space are at a premium.
5.6 Other Industrial Applications
Curved tooth gear couplings are also widely used in other industries, such as cement and concrete production, water treatment, and general manufacturing. In cement plants, they are used in mixers, conveyors, and rotary kilns, transmitting torque under heavy loads and high temperatures. In water treatment facilities, they are used in pumps and blowers, accommodating misalignments and ensuring reliable operation. In general manufacturing, they are used in various rotating equipment, such as machine tools, fans, and compressors.
6. Advantages and Limitations of Curved Tooth Gear Couplings
Curved tooth gear couplings offer numerous advantages over other types of couplings, but they also have certain limitations that need to be considered in practical applications. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application.
6.1 Advantages
One of the primary advantages of curved tooth gear couplings is their high torque transmission capacity. The curved tooth profile and optimized design allow them to transmit significantly higher torques compared to straight tooth couplings and other flexible couplings. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring high power transmission.
Another major advantage is their excellent misalignment compensation capability. Curved tooth gear couplings can accommodate axial, radial, and angular misalignments, which are common in most mechanical transmission systems. The spherical curvature of the external teeth ensures uniform load distribution across the tooth surface, avoiding edge pressure and reducing wear.
Curved tooth gear couplings also exhibit long service life. The use of high-quality materials and heat treatment processes, combined with the uniform load distribution, results in low wear and tear, ensuring the coupling can operate reliably for an extended period. Additionally, many curved tooth gear couplings are designed with excellent sealing systems, which prevent lubricant leakage and protect the tooth meshing area from contamination, further extending their service life.
Other advantages include compact structure, lightweight design, and easy installation. The optimized design of curved tooth gear couplings results in a compact and lightweight construction, making them suitable for applications where space and weight are limited. They can be installed both vertically and horizontally without the need for special tools, simplifying the installation process.
6.2 Limitations
Despite their numerous advantages, curved tooth gear couplings have some limitations. One of the main limitations is their lack of buffering and vibration damping capacity. Due to their rigid structure and absence of elastic elements, they cannot absorb shock loads or dampen vibrations effectively. This can lead to increased vibration and noise in the transmission system, potentially affecting the performance of other components.
Another limitation is their high requirement for lubrication. The tooth meshing area of curved tooth gear couplings requires adequate and appropriate lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Insufficient lubrication or the use of inappropriate lubricants can lead to dry friction, accelerated tooth wear, and even premature failure. Additionally, the lubricant needs to be selected based on the operating temperature, load, and environmental conditions, adding to the maintenance complexity.
Curved tooth gear couplings also have high requirements for installation precision. Improper alignment during installation can lead to uneven load distribution on the tooth surface, increasing wear and reducing the coupling's service life. Achieving the required installation precision often requires specialized tools and skilled personnel, which can increase the installation cost.
Finally, curved tooth gear couplings can generate additional loads and noise under certain operating conditions. In high-speed applications, the centrifugal force generated by the rotating components can create additional loads on the shafts and bearings. Additionally, the meshing of the teeth can generate noise, which may be a concern in applications requiring low noise levels.
7. Maintenance and Maintenance Strategies
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable operation and long service life of curved tooth gear couplings. The following are the key maintenance strategies:
7.1 Regular Lubrication
Lubrication is the most critical maintenance task for curved tooth gear couplings. It is essential to regularly check the lubricant level and quality, and replenish or replace the lubricant as needed. The type of lubricant should be selected based on the operating conditions, such as temperature, load, and speed. For high-temperature applications, high-temperature resistant lubricants should be used; for corrosive environments, anti-corrosive lubricants are recommended. The lubrication interval depends on the operating conditions, but generally, the lubricant should be replaced every 6-12 months.
7.2 Inspection and Monitoring
Regular inspection and monitoring of the coupling are necessary to detect potential issues early. During inspection, the following aspects should be checked: tooth surface wear, damage, or corrosion; tightness of connecting bolts; condition of sealing components; and alignment of the shafts. Vibration monitoring can also be used to detect abnormal operating conditions, such as misalignment or tooth wear. If any issues are detected, timely repairs or replacements should be carried out to prevent further damage.
7.3 Proper Installation and Alignment
Ensuring proper installation and alignment is crucial for the performance and service life of curved tooth gear couplings. During installation, the shafts should be aligned within the specified tolerance range. Specialized alignment tools, such as laser alignment tools, can be used to achieve precise alignment. The connecting bolts should be tightened to the specified torque to ensure a secure connection. Improper installation or alignment should be corrected immediately to avoid uneven load distribution and accelerated wear.
7.4 Environmental Protection
Protecting the coupling from harsh environmental conditions is also important. In dusty, wet, or corrosive environments, protective covers or seals should be used to prevent contamination of the tooth meshing area. Regular cleaning of the coupling surface is also recommended to remove dust, dirt, and other debris that may affect its operation.
8. Conclusion
Curved tooth gear couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, offering high torque transmission capacity, excellent misalignment compensation, and long service life. Their unique curved tooth design, robust construction, and diverse classification make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from power generation and metallurgy to oil and gas and aerospace. However, they also have limitations, such as the lack of vibration damping capacity and high requirements for lubrication and installation precision.
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the performance and service life of curved tooth gear couplings. By understanding the design principles, working mechanism, material selection, and maintenance strategies of these couplings, engineers and technicians can make informed decisions when selecting and using them in various industrial applications. As industrial technology continues to advance, curved tooth gear couplings are expected to undergo further optimization and improvement, adapting to the increasingly demanding requirements of modern mechanical systems.
« Curved Tooth Gear Couplings » Post Date: 2023/12/13
URL: http://www.rokee.com/en/tags/curved-tooth-gear-couplings.html